NEWS
-
 Published on 24/09/2013
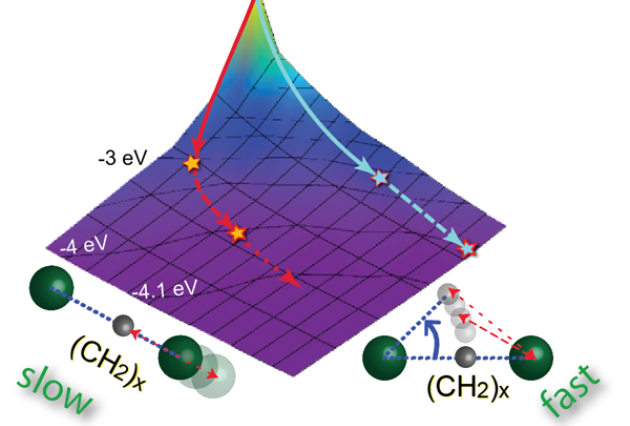
Published on 24/09/2013The forth way to dissociate
Dissociation is one of the simplest chemical reactions, where a molecule breaks apart into two or more fragments, i.e., other molecules, atoms, ions, or radicals. Understanding the mechanisms of (...)Read more -
 Published on 20/09/2013
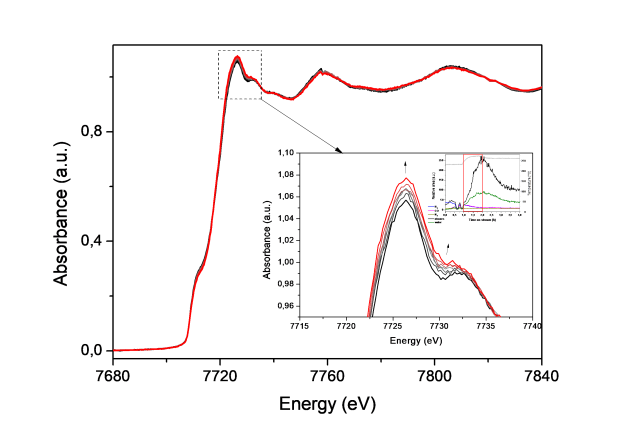
Published on 20/09/2013Quick-XAS and Raman operando characterisation of a cobalt alumina supported catalyst under (...)
The energy crisis driven by the long-term petroleum shortage, the growing demand for cleaner fuels and a more rational utilisation of resources (coal, natural gas, biomass…) are among the main reasons (...)Read more -
 Published on 19/09/2013
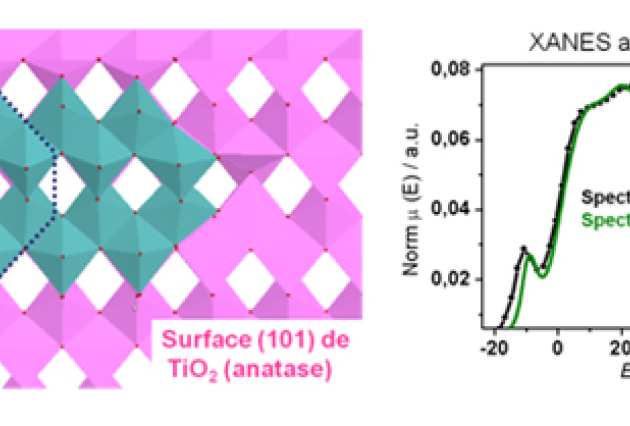
Published on 19/09/2013The structure of oxomolybdates TiO2-supported revealed by XANES spectroscopy
Supported molybdenum catalysts are widely used in their sulfide state in the treatment petroleum fractions, which are important economic and environmental issues. In their oxide states they can be (...)Read more -
 Published on 19/09/2013
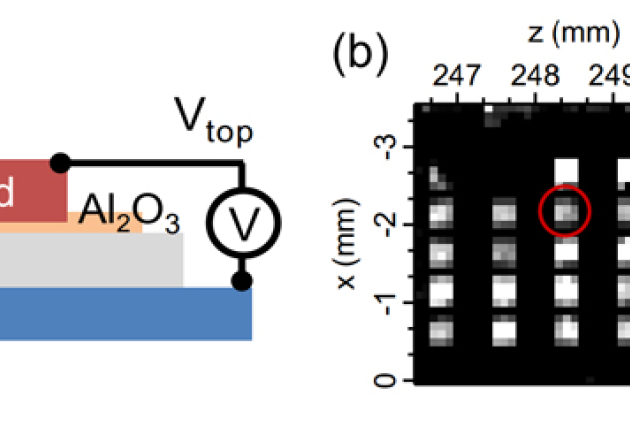
Published on 19/09/2013Data storage – Properties of ferroelectric materials studied by XPS/PEEM
Ferroelectric memory devices could be an alternative to magnetic based memories for future high-density data storage. Such devices have considerable advantages: they are non-volatile, have fast read (...)Read more -
 Published on 19/09/2013
Published on 19/09/2013How interactions alter the number of electrons in iron-based superconductors
In 2008, a new family of superconductors was discovered, based on square planar iron. This attracted the attention of many physicists because superconductivity was found to occur up to relatively high (...)Read more -
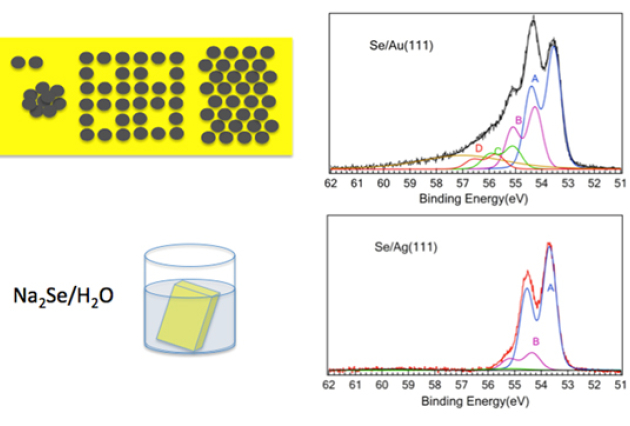 Published on 12/09/2013
Published on 12/09/2013Selenium adsorption on coinage metals: chemisorption, polymerization and selenide films
Selenides e.g. bulk silver selenide are of much interest because of their use in various applications such as a thermoelectric materials, a photosensitizer in photography, in photochargeable batteries (...)Read more -
 Published on 27/08/2013
Published on 27/08/2013Molecular refrigerators
Experiments performed at DEIMOS beamline by a team of researchers of the Italian National Research Councils (CNR), the University of Manchester and French CNRS found that a single molecule may well (...)Read more -
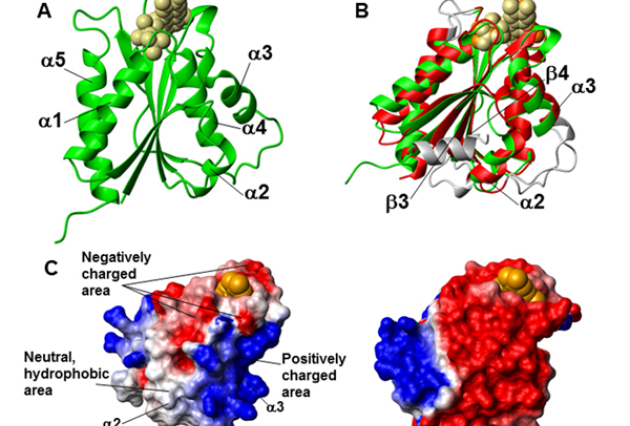 Published on 27/08/2013
Published on 27/08/2013Molecular view of an electron transfer process essential for Fe-S protein biogenesis
Iron-sulfur clusters are ubiquitous cofactors made of iron and inorganic sulfur. They are essential for the function of proteins involved in a great range of activities: electron transport in (...)Read more -
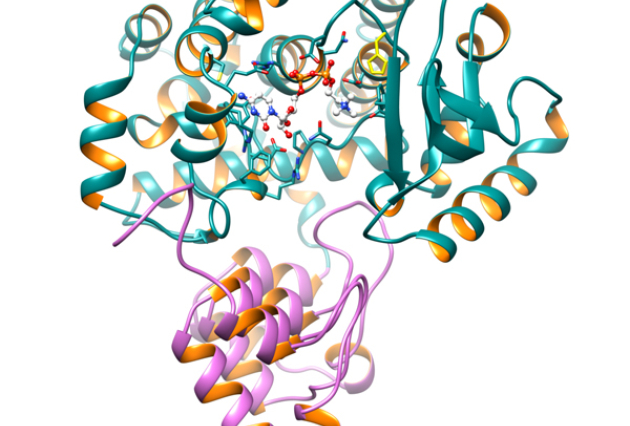 Published on 27/08/2013
Published on 27/08/2013How the Legionella bacterium hijacks a regulator of membrane traffic in infected cells
Legionella pneumophila, which causes the Legionnaire’s disease, escapes destruction by the immune system by hiding inside the infected cell. This camouflage strategy requires that the bacterium (...)Read more -
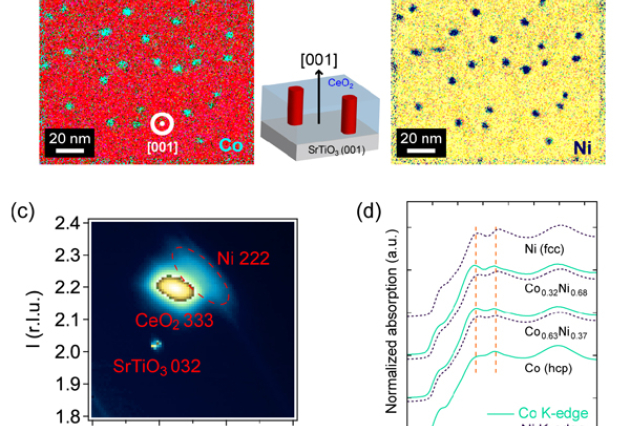 Published on 27/08/2013
Published on 27/08/2013Self-assembled vertically aligned epitaxial ferromagnetic alloy nanowires: a combinatorial (...)
Researchers at the Paris NanoSciences Institute (CNRS-UPMC), in collaboration with groups at SOLEIL and UVSQ, have developed a new technique for growing epitaxial alloy nanowire arrays in a matrix (...)Read more -
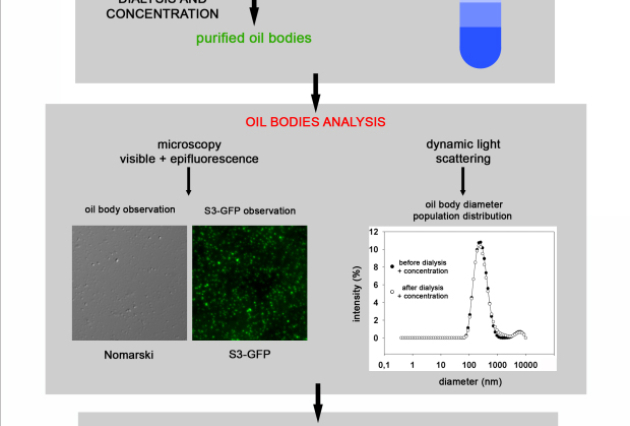 Published on 26/08/2013
Published on 26/08/2013Plant oils and their derivatives. Structural study of an oleosin, a protein at the heart (...)
In the current context, with fossil fuels running out and high priority of environmental protection, the valorization of oil from biomass for energy and green chemistry is of increasing interest. The (...)Read more -
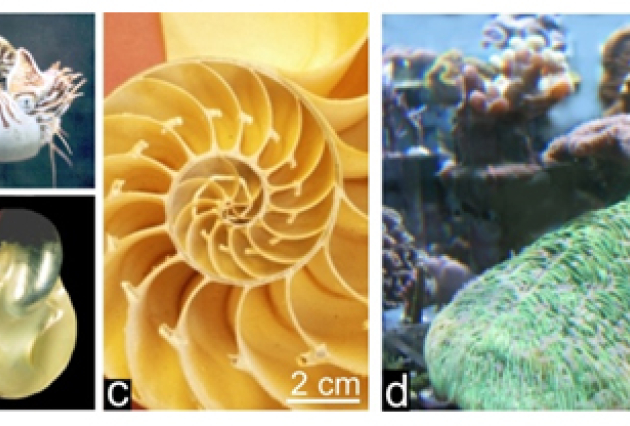 Published on 17/07/2013
Published on 17/07/2013How do living organisms make mineral structures? At TEMPO beamline, X photoemission on (...)
X photoemission spectroscopy experiments carried out on TEMPO beamline provide the first direct and measurable evidence of an existing link between the organic and mineral phases of calcareous (...)Read more
