NEWS
-
 Published on 26/10/2017
Published on 26/10/2017Illuminating the composition of carbon-based ancient materials
Carbon can take various forms depending on the function of the molecule in which it is placed, each with its own distinct ‘species’. The ‘speciation’ of carbonaceous materials is generally obtained by (...)Read more -
 Published on 20/10/2017
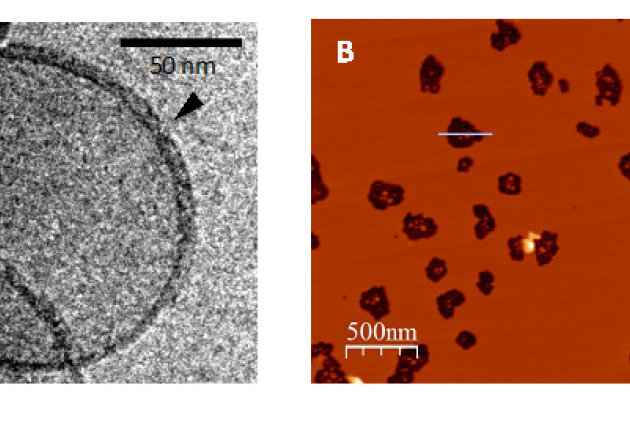
Published on 20/10/2017Functional amyloids and bacterial adaptation
To survive in their environment, bacteria must adapt to very different growth conditions. One way of doing this is by use of a protein called Hfq which forms complexes with specific small ribonucleic (...)Read more -
 Published on 06/10/2017
Published on 06/10/2017VR 360° visit of Synchrotron SOLEIL
Visit SOLEIL ... without moving!Read more -
 Published on 05/10/2017
Published on 05/10/2017Low photon flux Macromolecular Crystallography experiments are possible at kHz frame rates (...)
In September 2017, a team from ELI Beams (Extreme Light Infrastructures, Prague, Czech Republic), together with participants from IBT-Biocev (Institute of Biotechnology, Vestec near Prague, Czech (...)Read more -
 Published on 21/09/2017
Published on 21/09/2017Correlation between structures and electronic properties in PAH clusters
Astrophysicists think that polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) are widely present in interstellar space. Nevertheless, their mechanisms of formation by evaporation from carbonaceous nanograins are (...)Read more -
 Published on 31/08/2017
Published on 31/08/2017SOLEIL is a member of Respore, a Major Research Domain (“Domaine d'Intérêt Majeur”, DIM) (...)
The Synchrotron SOLEIL is a member of Respore (“Réseau d'Excellence en Solides Poreux”, Network of Excellence in Porous Solids ) , a research network dedicated to analyzing and characterizing porous (...)Read more -
 Published on 25/08/2017
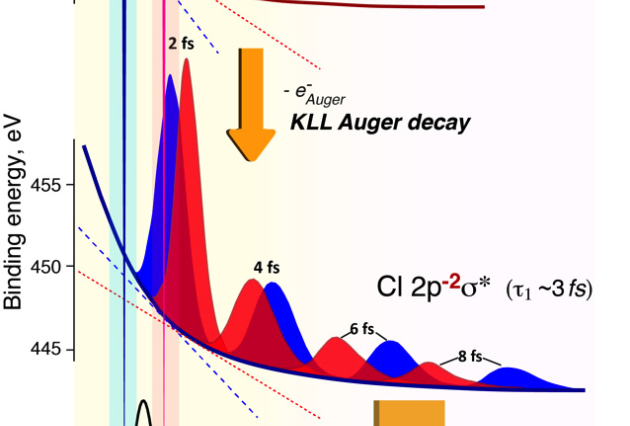
Published on 25/08/2017Fast track for ultrafast processes: controlling molecular dissociation on attosecond (...)
By carefully choosing the photon energy for the excitation of the deep-core 1s electron in HCl to the dissociative σ* orbital, scientists from France (UPMC/CNRS and SOLEIL), Germany (Berlin University (...)Read more -
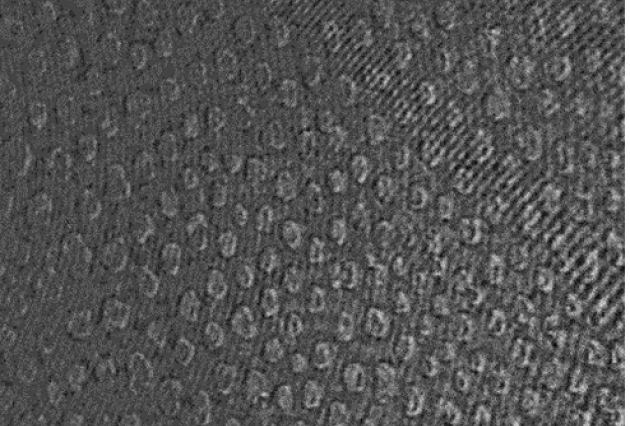 Published on 03/08/2017
Published on 03/08/2017A biomembrane model helps to understand the effects of amoxicillin on cells
Amoxicillin (AMX) is an antibiotic whose mechanism of action promotes cell wall lysis and consequently the death of bacteria from several different species. AMX is considered a first-line drug against (...)Read more -
 Published on 19/07/2017
Published on 19/07/2017Visits General Public
Exceptionally, SOLEIL will open its doors to the public during summer time!Read more -
 Published on 17/07/2017
Published on 17/07/2017SOLEIL Highlights 2016
A decade of beams at SOLEIL: 2016 is a year of anniversaries, shared with an ever increasing number of users on our beamlines. Twenty eight beamlines have now received photons, since the X-ray beam (...)Read more -
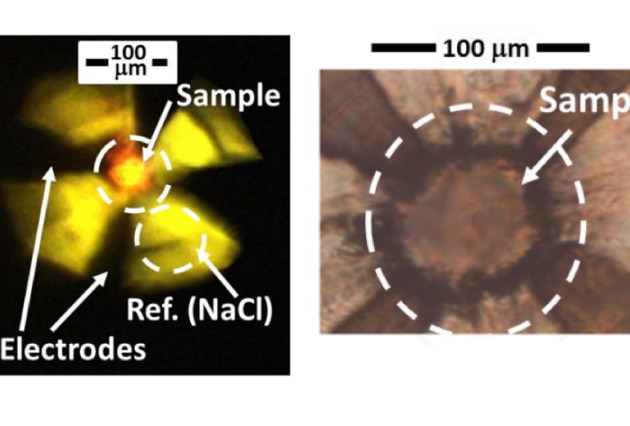 Published on 12/07/2017
Published on 12/07/2017The mechanism of superconductivity at record temperature confirmed by infrared (...)
The absence of electrical resistance in superconducting materials gives them an enormous interest in terms of applications, in the fields of energy and transport, for example. Until now, however, the (...)Read more -
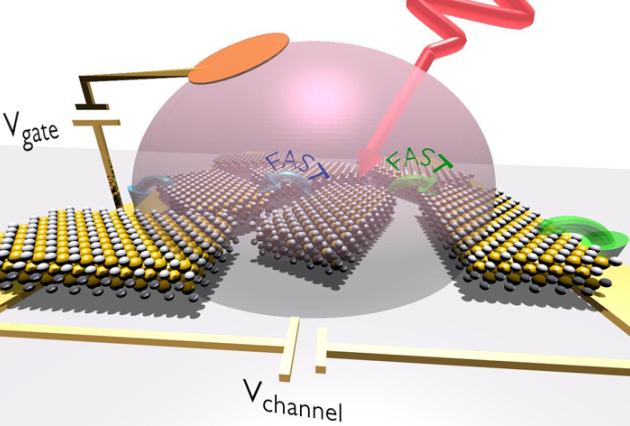 Published on 11/07/2017
Published on 11/07/2017Towards nanocrystal-based infrared photodetectors: study of the transport dynamic in (...)
Over the last 20 years, colloidal nanocrystals have excited the interest of researchers because of their luminescence properties or, more recently, their use as a light source for displays. However (...)Read more
