Probing spin-spin
interactions in surface-
supported single-molecule
magnets
The ability of X-ray Magnetic Circular
Dichroism (XMCD) to detect magnetism
in an element-specific manner was exploited
for a temperature-dependent study
of Fe
3
Cr single-molecule magnets deposited
on a Au(111) surface. The dichroic signals
recorded at Fe and Cr L
3
edges over
a broad temperature range provided
the Fe-Cr superexchange-coupling constant,
which conforms to the bulk-phase value
in both sign
and
magnitude. Our data
indicate that interaction with the surface
has no significant influence on
intramolecular spin-spin coupling.
Single-molecule magnets (SMMs) are
metal-ion based molecules of special
importance in the emerging field
of molecular scale electronics. In these
systems, an anisotropy barrier slows down
the reorientation of magnetic moment,
so that magnetic blocking is observed
at low temperature (
T
) [1]. According
to recent theoretical predictions, spin
detection and manipulation are possible
by driving a spin-polarized electric current
through an individual SMM in a STM
experiment [2]. It is thus important to
deposit SMMs on conducting substrates
in such a way that they remain structurally
and functionally intact. After years of
unfruitful work on Mn
12
SMMs, in 2009
an XMCD experiment finally revealed
magnetic blocking in surface-wired
tetrairon(III) (Fe
4
) complexes [3]. In these
small SMMs, superexchange interactions
between the nearest-neighboring iron(III)
ions (
s
= 5/2) are antiferromagnetic (AF)
and afford a
S
= 5 ground state
(Figure
➊
a
). A proper design of molecular
structure further allowed the preparation
of partially-oriented monolayers which
displayed spectacular waist-restricted
hysteresis loops and clear signatures
of resonant quantum tunneling effects [4].
Introduction
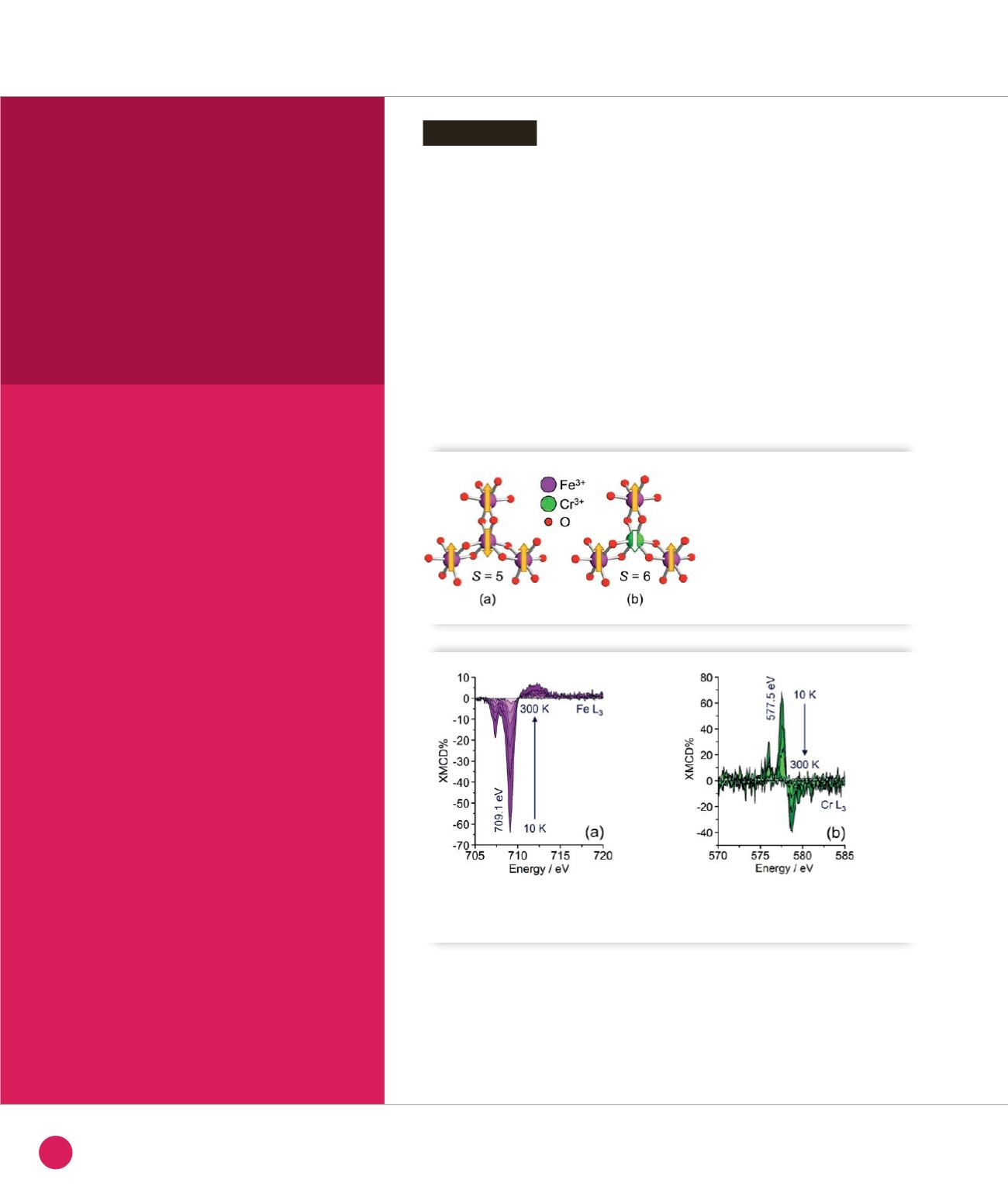
➊
Metal-oxygen core in Fe
4
(
a
) and Fe
3
Cr (
b
)
SMMs. Arrows depict the spin arrangement
in the ground state with total spin
S
. The core
is surrounded by organic ligands that provide
terminal coordination to Fe ions and Fe-Cr
bridging.
CHEMISTRY AND PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY, NANOCHEMISTRY
➋
T
-dependent XMCD spectra at the Fe L
3
(a) and Cr L
3
(b) edges measured on a monolayer of Fe
3
Cr on Au(111).
Spectra have been recorded at 50 kOe and normalized with respect to the L
3
maximum in the corresponding
isotropic XAS spectrum.
44
SYNCHROTRON
HIGHLIGHTS
2013


