Influence of the surface structure on the magnetic properties of Zn1-xCoxO
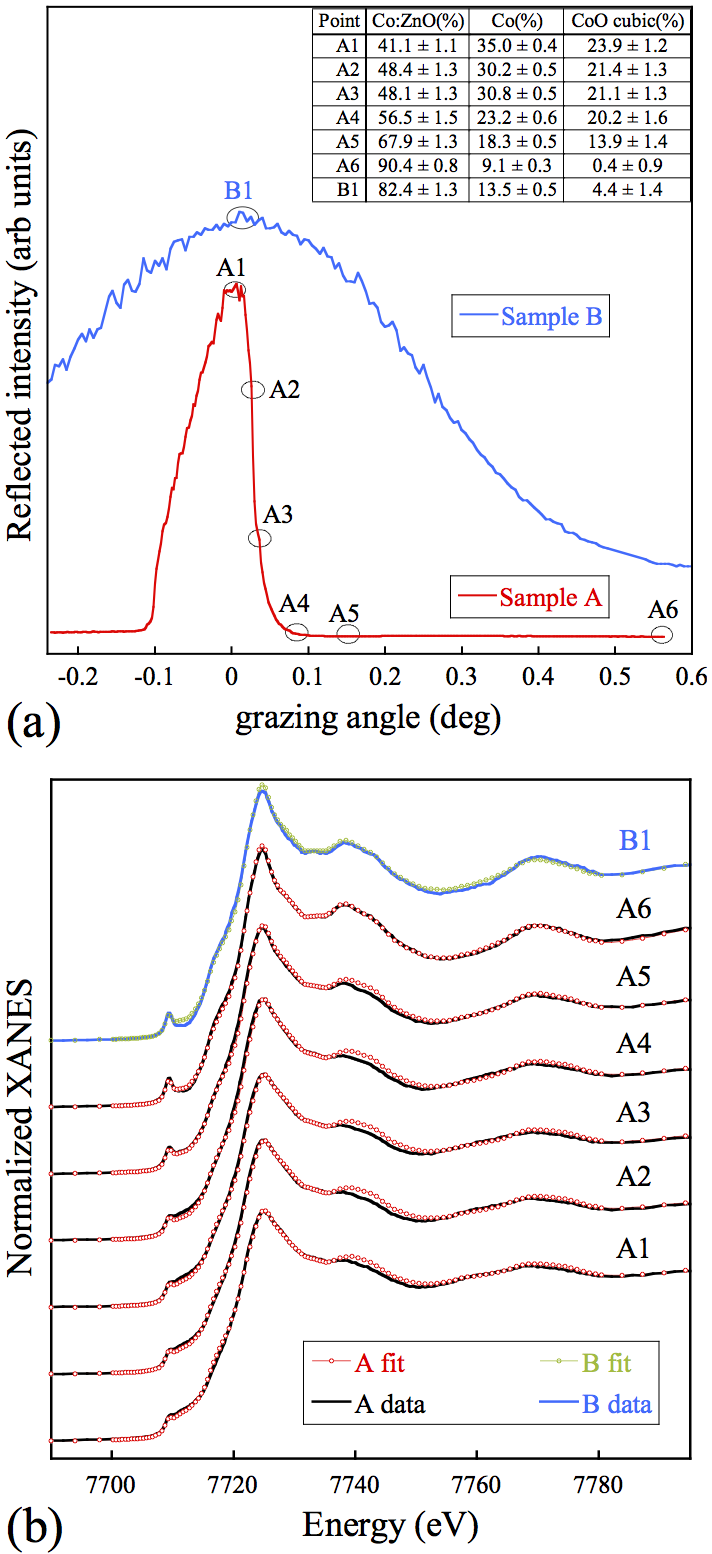
The surface of ferromagnetic Zn1-xCoxO wurtzite epilayers has been studied by coupling atomic force microscopy and advanced x-ray spectroscopy. It was found that, even in high-quality epilayers, the formation of Co clusters and iso-space-group Co-rich regions can take place at the sample surface while the bulk maintains random Co distribution. Comparing structural characterization with magnetometry, it was shown that these surface modifications are not at the origin of the magnetic properties of the material. Quite the reverse, ferromagnetic behavior is enhanced in the sample characterized by the less defective surface.