SAMBA

SAMBA (Spectroscopie Appliquée aux Matériaux Basée sur l'Absorption) est une ligne d'absorption dans le domaine des rayons X durs. SAMBA est ouverte a une vaste communauté scientifique qui va de la physique à la chimie, les sciences des surfaces et de l'environnement.
L'équipe

* Prestataire extérieur, intérimaire ou collaborateur
Les actualités
Toutes les actualités
Prix de la meilleure thèse attribuée à Francesco Paparoni par le Journal PhysChem

Suivre les dommages thermiques dans les cellules tumorales
Données techniques
- Domaine en énergie
-
Entre 4.8 et 40 keV
- Résolution en energie (ΔE/E)
-
Si(220) : 6x10-5 @ 15 keV
- Source
-
Aimant de courbure Radiation (Ec = 8.65 keV) 1.5 mrd Horizontal x 1 mrd Vertical
- Flux in the XAS hutch
-
Si(220) : 2.8x10+11 Phot/s/0.1%bw @ 15 keV
Si(220) : 2.3x10+10 Phot/s/0.1%bw @ 35 keV
- Optics
-
Un monochromateur sagital focalisant entre deux miroirs cylindriques et courbables
- Beam size at sample (EXAFS hutch)
-
200x300 μm2
- Beam size at sample (SurfAs hutch)
-
300x300 μm2
- Detecteurs
-
Transmission: Chambres à Ionisation (Oxford)
Fluorescence: Un détecteur Ge monolitique 35-elements (Canberra), ou un détecteur SDD 13 éléments (Mirion)
Rendement Total d'Electrons
Thématiques scientifiques
Science des matériaux/ Stockage d'énergie | Détermination des propriétés structurelles et électroniques, tailles moyennes de systèmes nanométriques. Etudes statiques ou dynamiques de matériaux nouveaux, type anode ou cathode. Compréhension des transitions de phase magnétiques dans les systèmes moléculaires étudiés en chimie de coordination. Caractérisation de verres, etc… |
|---|---|
| Physique | Caractérisation d’amas, intégrés dans des matrices |
| Biologie & Biomatériaux | Etudes de la réactivité de composés biomimétiques utilisés comme composés modèles pour comprendre le mécanisme catalytique de systèmes plus complexes (ex: systèmes metallo-enzymatiques). Investigation d’ions métalliques présent dans des metalloprotéines ou dans des complexes bioinorganiques. |
| Sciences de la Terre et Environnementales | Caractérisation chimique de l’environnement local des métaux/métalloïdes présents dans les systèmes naturels (sols, sédiments, plantes, aérosols, microorganismes, etc…) |
| Sciences des surfaces | Caractérisation de la structure locale de couches minces à l’étape initiale de croissance. Etude des interfaces: métal/métal, métal/semiconducteur, ou oxide/métal |
| Catalyse | Caractérisation électronique et structurale de catalyseurs pour comprendre/prédire leur activité catalytique et leur sélectivité pour une réaction donnée (catalyseur DeNOx, Fischer-Tropsch, hydrodegenation d’hydrocarbones…) |
Cabane Optique
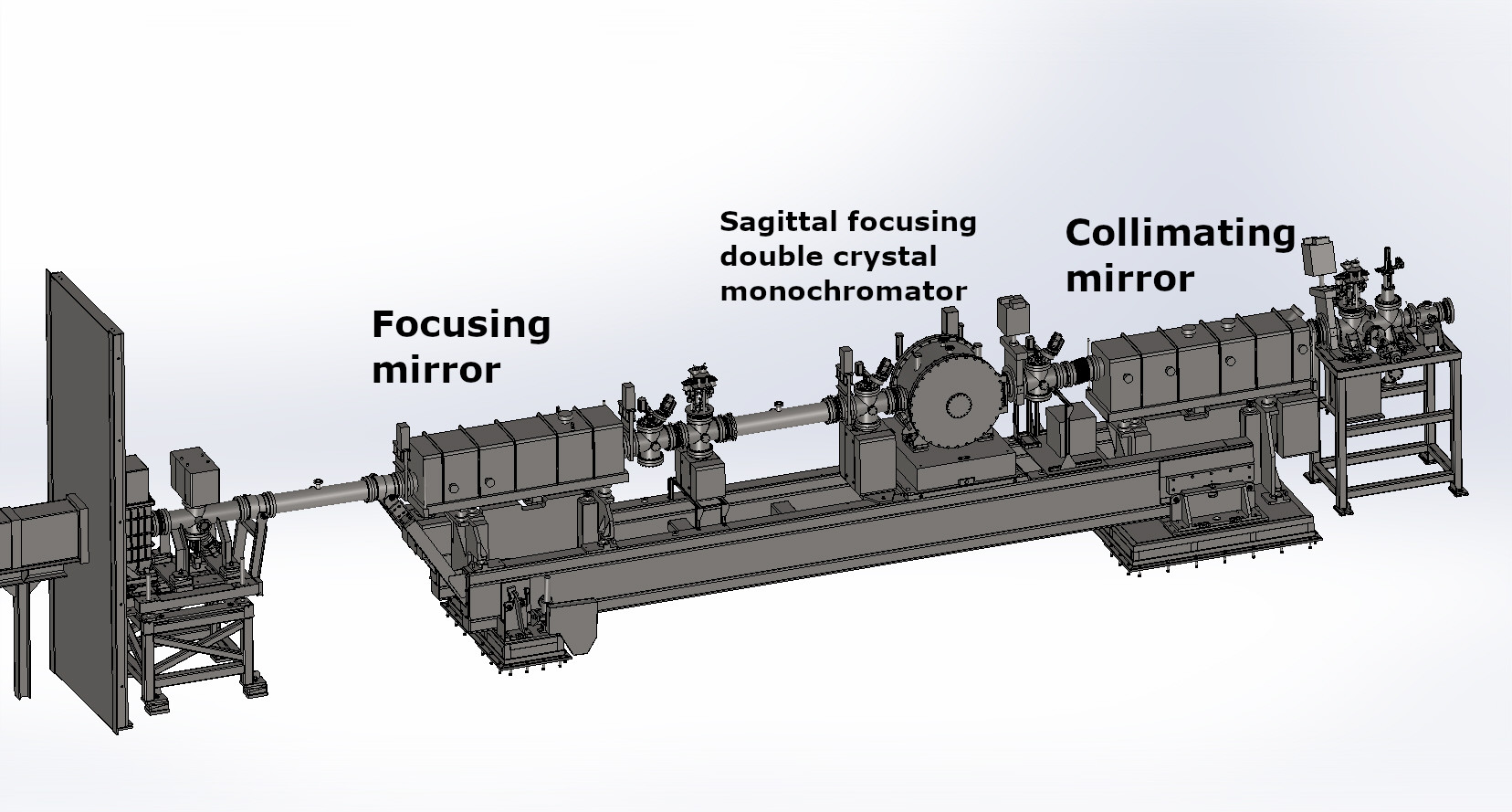
Schéma de la cabane Optique
Miroirs
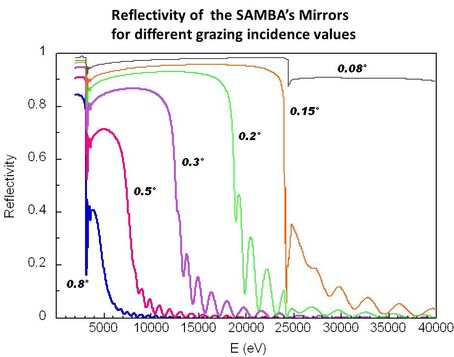
Deux miroirs en silicium cylindriques et courbables (WinlightX), recouverts d'une couche de 50 nm de Pd, sont utilisés pour:
- La collimation verticale du faisceau
- La focalisation verticale du faisceau à la position de l'échantillon
- Le réjet harmonique
Les miroirs sont utilisés sur toute la gamme en E (4-40 keV) couverte par la ligne, en les inclinant de 10 à 1 mrad (c.a.d. de 0.57° à 0.057°) en fonction de l’énergie nécessaire pour satisfaire le rejet harmonique.
The reflective Pd surfaces are 1200 mm long per 88 mm wide allowing a horizontal acceptance of about 6.2 mrad on the first collimating mirror located at 14.1 m from the source. The surface of the mirrors was polished to a rms roughness less than 3 Ǻ rms and to a longitudinal slope error less than 2µrad rms. The first mirror is water cooled using blades immersed in In-Ga eutectic in grooves in the mirror surface.
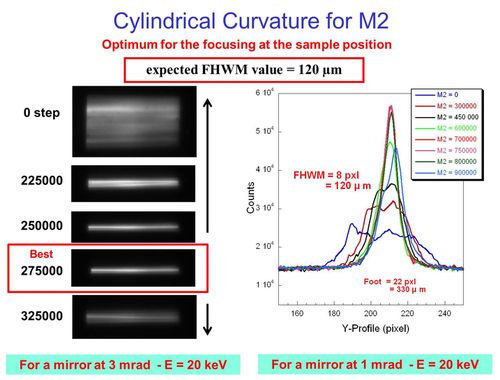
The focusing in the vertical direction is ensured by the M2 mirror, the resulting vertical spot size at the sample position is 110 µm (FWHM) with a foot size of about 300 µm.
Sagittal focusing double crystal monochromator

Sagittal focusing double crystal monochromator
The sagittally focusing Double Crystal Monochromator (DCM) provided by Oxford Danfysik is used in the so-called high flux mode. The DCM is installed at 16.1 m from the source. It deals of a first flat water-cooled Si(220) crystal and a sagittally bent 2nd crystal. The main Bragg axis of rotation passes through the centre of the diffracting face on the 1st crystal and perpendicular to the beam axis. In this way, the incident white beam is always centred on the axis of rotation. A fixed offset to the exit beam is achieved by moving the 2nd crystal perpendicularly to the first one according to the Bragg angle. In this case the beam moves along the axis of the sagittally-bent 2nd crystal. The first crystal is indirectly water-cooled by using a multi-channel water cooling support (SOLEIL original design) in contact with the crystal through a thin film of In-Ga eutectic. The 2nd crystal is uncooled.
The horizontal acceptance of the monochromator is limited by the efficiency of the sagittal bender. For a horizontal acceptance of 1.5 mrad, the typical beam size at the sample position is around 300 µm (H) x 200 µm (V) (FWHM).
In order to avoid possible radiation damage on the sample due to the high density of photons in a so small spot, the beamline is often slightly defocused in both directions to achieve a spot size of 2 mm (H) x 1mm (V).
Then the typical flux at the sample position at 8.5 keV is 5x1011 ph/s with the Si(220) DCM (6 mrad of vertical acceptance and 1.5 mrad of horizontal acceptance, I = 400 mA).
Related publications:
SAMBA: The 4-40 keV X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy Beamline at SOLEIL.
V. Briois, E. Fonda, S. Belin, L. Barthe, C. La Fontaine, F. Langlois, M. Ribbens, F. Villain
UVX 2010 - 10e Colloque sur les Sources Cohérentes et Incohérentes UV, VUV et X ; Applications et Développements Récents: 41-47. EDP Sciences 2011
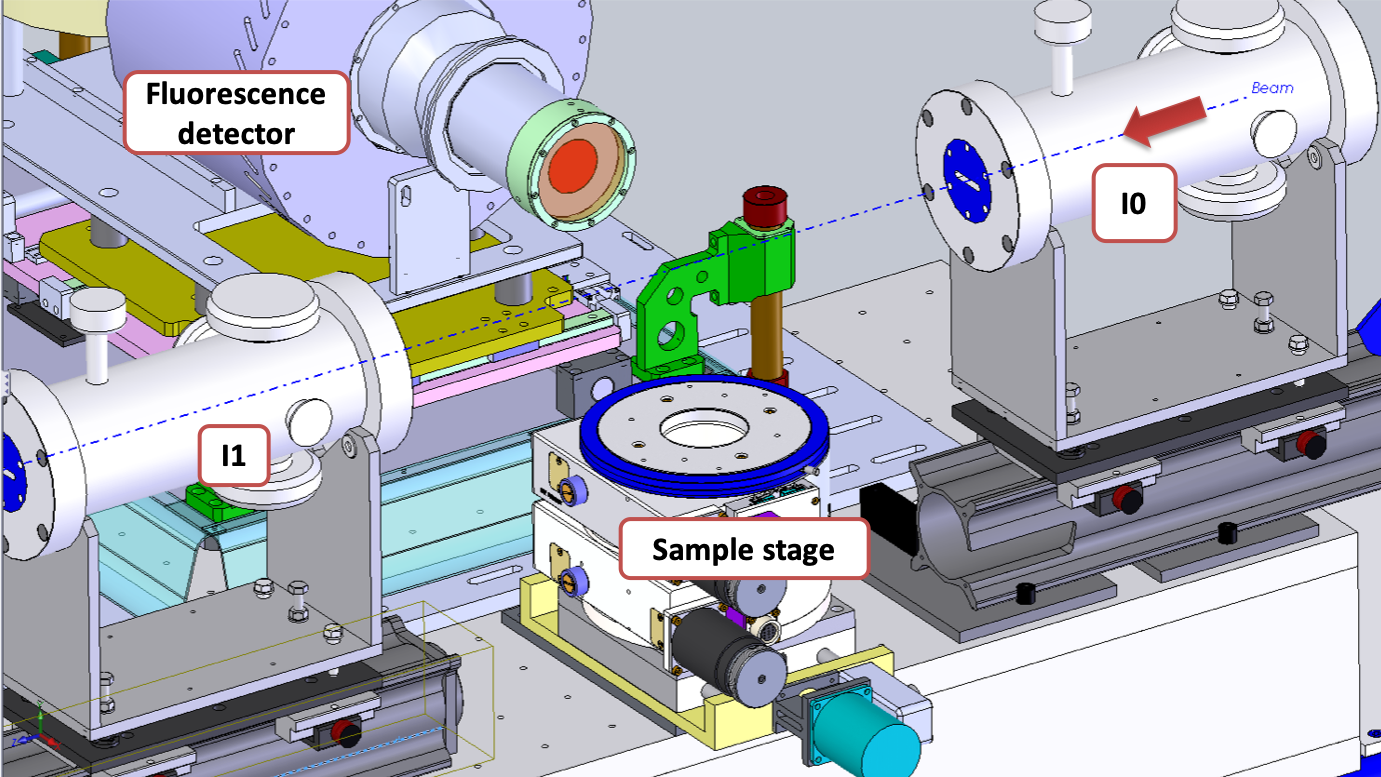
EXAFS Hutch
Detection
Transmission :

Oxford ionization chambers
Fluorescence :
Canberra 35-elements monolithic planar Ge pixel array detector

Detector Silicon Drift : Vortex
Total electron yield
No picture. The sample must be electrical conductor otherwise a thin layer of graphite may be evaporated.
Setups disponibles
Catalysis
Gas blower
quartz capillary oven for operando measurements up to 850°C and 10-15 bars
Gas distribution system

- Complex mixtures
- Humidifier
- Heated lines
- Remote control
Low temperature
He cryostat suitable for transmission and fluorescence detection (20 K to 500K). Liquid nitrogen (80 K) can also be used
Grazing incidence
- Sample T° : 900°C
- T° Ramp : 10 à 30°C/min
- Pressure: 5.10-7mbar
- possible to work under partial gas pressure
- Modes Transmission (Reflexafs) and Fluorescence possible
Liquid Cells
We have cells with different optical path available for basic or acidic solution. Kapton, Mylar, PP or PTFE can be used as windows depending of the nature of the solution.

Other
The experimental hutch can host different setups and sample environments provided by the beamline, such as potentiostats, mass spectrometer, micro GC, Raman, UV-visible, differential scanning calorimeter, and other equipment provided by users. Please contact the beamline staff to discuss any other setups.
Informations aux utilisateurs, préparation des échantillons, la charte SOLEIL des utilisateurs et une aide à la soumission de projets sont disponibles en ligne.
Gas
The application for the use of specialty gases must be stipulated in your proposal in order that the security service can assess the associated risks. Specialty gases must be commanded 8 weeks before your experiment, also you have to prevent your local contact well in advance, for common gases (helium, argon, nitrogen, hydrogen, air and oxygen) only 4 weeks are sufficient.
Liquid Helium
The application for the use of liquid helium must be stipulated in your proposal and recalled to your local contact in such a way to order sufficiently in advance the suitable volume. Please, given the high cost of liquid helium, carefully consider its use.
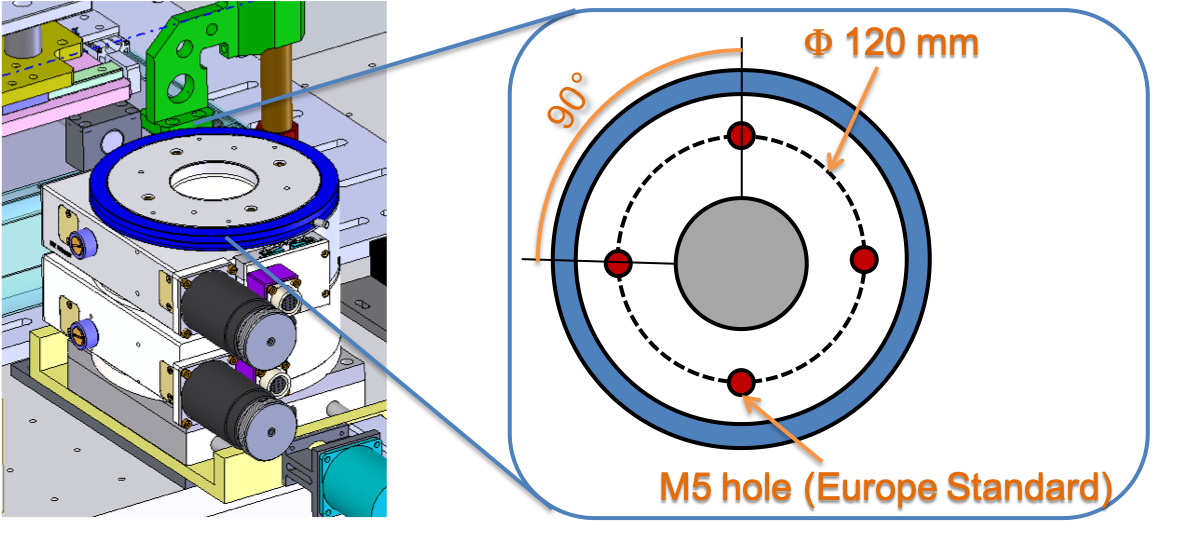
Sample positioning
Aide à la soumission de projets
Dépôt de projets
Date limite (standard & BAG project) :
15 Février - 15 septembre
Comment préparer votre demande de temps de faisceau ?
Les soumissions de projet doivent suivre le modèle prédéfini suivant : Renseignement du "formulaire" en ligne, concernant la partie générale du projet.
- Description scientifique et expérimentale
- Annexes des images (format .jpeg .png)
- Description des conditions expérimentales nécessitant des précautions spéciales de sécurité
- Soumission du projet
(S'il s'agit de la continuation d'un projet, il est nécessaire de soumettre un rapport d'expérience(s) passée(s) dans le SUN set et inclure la (les) publication(s) correspondante(s) avant de soumettre votre nouveau projet)
L'ensemble de la demande doit être rédigé en anglais
De plus,
- Il est nécessaire de contacter un des scientifiques de la ligne, pour discuter de l'adéquation du projet avec les spécificités de la ligne de lumière en particuliers au sujet des environnements échantillons, du mode de détection ou d'acquisition.
- La justification du temps de faisceau demandé est indispensable.
N'oubliez pas de mentionner vos publications liées à la ligne dans le sunset.
Pour plus d'informations : Le guide général des Utilisateurs
12/01/2026
C'est avec grand plaisir que nous pouvons annoncer le prix de la meuillere thèse 2025 attribué au Dr. Francesco Paparoni par le journal Phys Chem de MDPI publishing : https://www.mdpi.com/journal/physchem/awards/3130.
Francesco a developpé sa thèse entra l'université de Camerino et le Synchrotron SOLEIL, il est maintenant en contrat de post doc au sein de l'équipe SAMBA .
Congratulations,
Francesco.
----------------------------------
24/06/2025
Notre manuscrit présentant notre logiciel de traitement de données XAFS « Fastosh » a été publié. Ceci est la référence permanente du code. Elle doit être utilisée pour citer le logiciel.
----------------------------------
2024
Notre récent article qui décrit Une nouvelle cellule électrochimique pour des études XAS en mode operando sur des supports opaques aux rayons X a été sélectionné par les éditeurs de PCCP comme un article HOT de PCCP en 2024. Vous pouvez trouver la collection ici

Logiciel de traitement de données XAFS, pour Windows, Mac, ou Linux.
Reference permanente pour citation:
Landrot & Fonda, "Fastosh: a software for the treatment of XAFS datasets of environmental relevance or acquired in operando conditions", J. Synchrotron Rad. (2025). 32(4), 1085-1094
Dernière Version (27/11/2025) : Fastosh v 1.0.10
Voir description de la dernière version dans le fichier « Version description »
Abonnement à une liste de diffusion pour être informé des nouvelles mises à jour:
Attention: par mesure de sécurité, l’abonnement doit être confirmée une seconde fois en utilisant le lien dans le message « Subscribing to Fastosh » envoyé dans la boîte de messagerie personnelle après confirmation d’abonnement sur le site SYMPA
https://groupes.renater.fr/sympa/info/fastosh
Fastosh propose des fonctionnalités originales pour tous les utilisateurs de la technique XAFS :
- Chargement rapide de plus de 100 spectres XAFS (données ASCII OK)
- Affichage automatique de la moyenne et de l’estimation du bruit aléatoire; alignement automatique des données
- Moyennage par sous-groupe pour un jeu de données spécifique
- Analyse par composantes principales (PCA), « Target Transformation », et MCR-ALS
- Combinaisons linéaires: un échantillon avec multiples jeux de références, ou multiple échantillons avec un jeu de références
- Filtrage d'un jeu de données dans deux directions (energy and tile directions)
- Différentes approches pour retirer les artefacts dans les spectres
- Création facile de figures en 3D
- Transformation de Fourier ou par ondelette de l'EXAFS. Interpretation du chi, FT, et carte WT via un outils utilisant FEFF8L (inclus dans Fastosh)
Et des fonctionnalités spécifiquement pour les utilisateurs de SAMBA :
- Visualisation de toutes les données de fluorescence sauvées en fichiers SAMBA HDF
- Extraction de spectres XAFS optimisés sans artefacts en exploitant les données pixels du détecteur fluo et spectres MCA
- Accès à toutes les données contextuelles relatives à chaque spectre (positions moteurs, paramètres de scan et dcm, etc...)
- Affichage des données correspondantes à chaque "ascan" ou "dscan" collecté lors d'une campagne de mesure, à l'aide d'une fenêtre interactive
Mac Installer
Linux Installer
Version Description (PDF)