GALAXIES

The GALAXIES beamline is dedicated to inelastic x-ray scattering (IXS) and hard x-ray photoemission (HAXPES). These spectroscopic techniques are powerful probes to characterize the electronic properties of materials. The beamline is optimized to operate in the 2.3 - 12 keV energy range with high resolution and micro beam.
GALAXIES comprises of two endstations for RIXS and HAXPES
Scientific opportunities
| Quantum materials |
Strongly correlated electrons Superconducting materials Mixed valent compounds; heavy fermions Oxide heterostructures ; interfaces |
|---|---|
| Energy materials, catalysis |
Metal complexes Chemical analysis in-situ Catalysis, electrochemistry |
| Extreme Conditions |
Phase transition under high pressure K-edge of light elements |
|
Dilute Matter, Liquid phases |
Chemistry in solution Ultrafast molecular dynamics |
| Cultural heritage materials |
Chemical speciation Imaging |
Beamline news
All GALAXIES's news
SOLEIL Highlights 2024

SOLEIL's contribution to the Energy Transition
Team
* External service provider, temporary or collaborator
Associates and Partners
Employment
access to the SOLEIL employment web page
Technical data
- Energy range
-
2.3 – 12 keV
- Resolution
-
ΔE from 100 meV to 1 eV at 8 keV
- Source
-
In-vacuum U20 undulator
- Polarization
-
linear (H)
linear (V), circular with a quarter wave plate
- Spot size
-
20 (V) x 80 (H) µm2 in standard mode, 5 (V) x 10 (H) µm2 in KB configuration
- Optics
-
2-bounce fixed-exit monochromator Si111, DCM
4-bounce high-resolution monochromator (Si220 symetric and asymetric), HRM
Collimating and focusing mirrors; 2 mirrors in KB configuration
- Flux
-
1.5x1012 ph/s (standard foc.), 5x1011 (micro-foc.) at 8 keV
- Detectors
-
Pixelated detectors
Si drift diodes
Avalanche diode
- Instrument
-
RIXS : 1-2m radius IXS spectrometer ; 0.5-1 m radius multi-analyzer setup (4x1 or 2x2)
HAXPES : high energy / high resolution electron analyzer (30 meV à 12 keV)
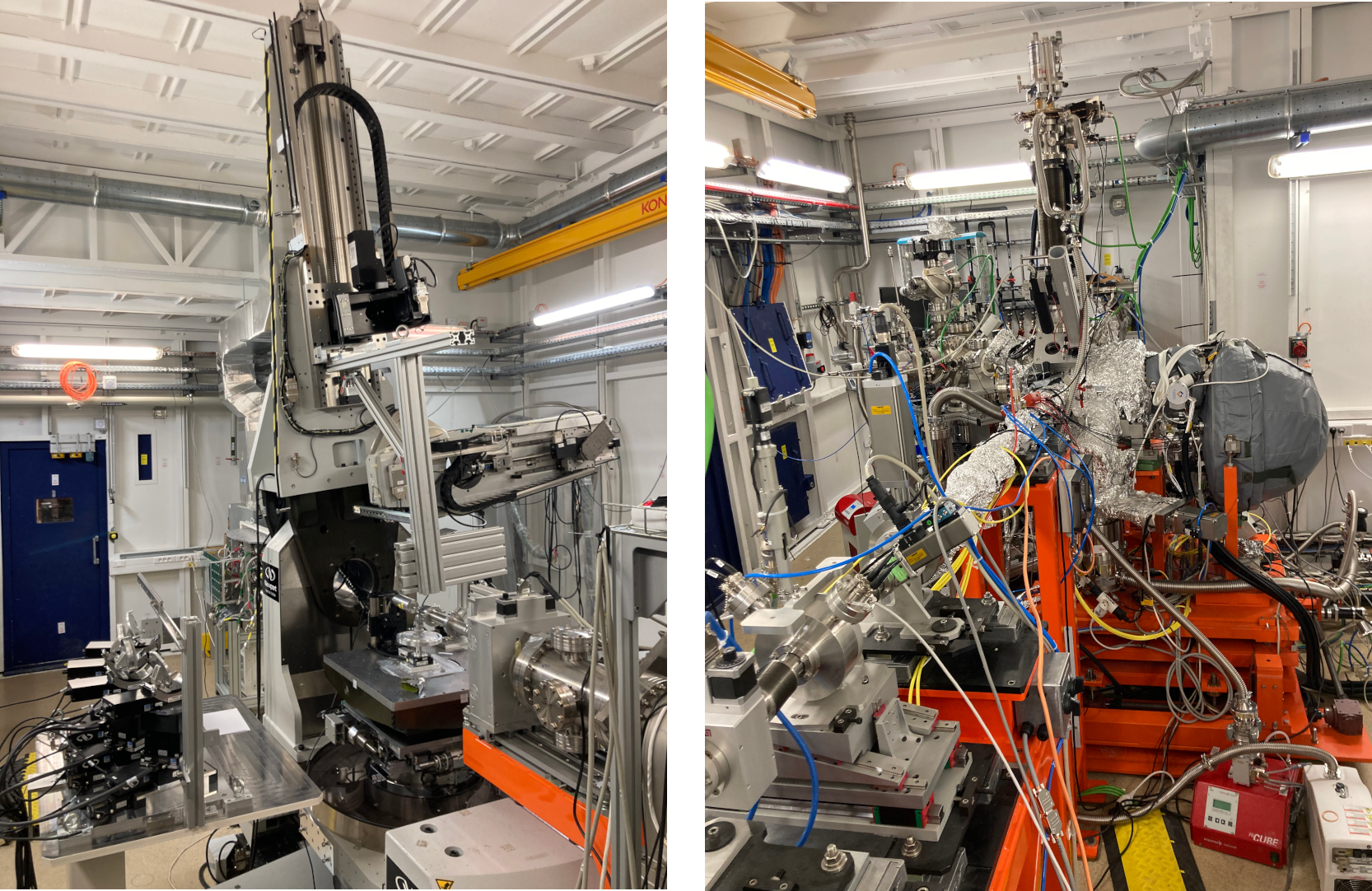
Layout
RIXS
IXS / RIXS / XES / RXES / HERFD-XAS
RIXS endstation
Energy range : ~4-12 keV
Spot size : 80 x 30 μm2 (H x V) [mode M2B] or 15 x 15 μm2 (H x V) [mode KB]
Includes several instruments

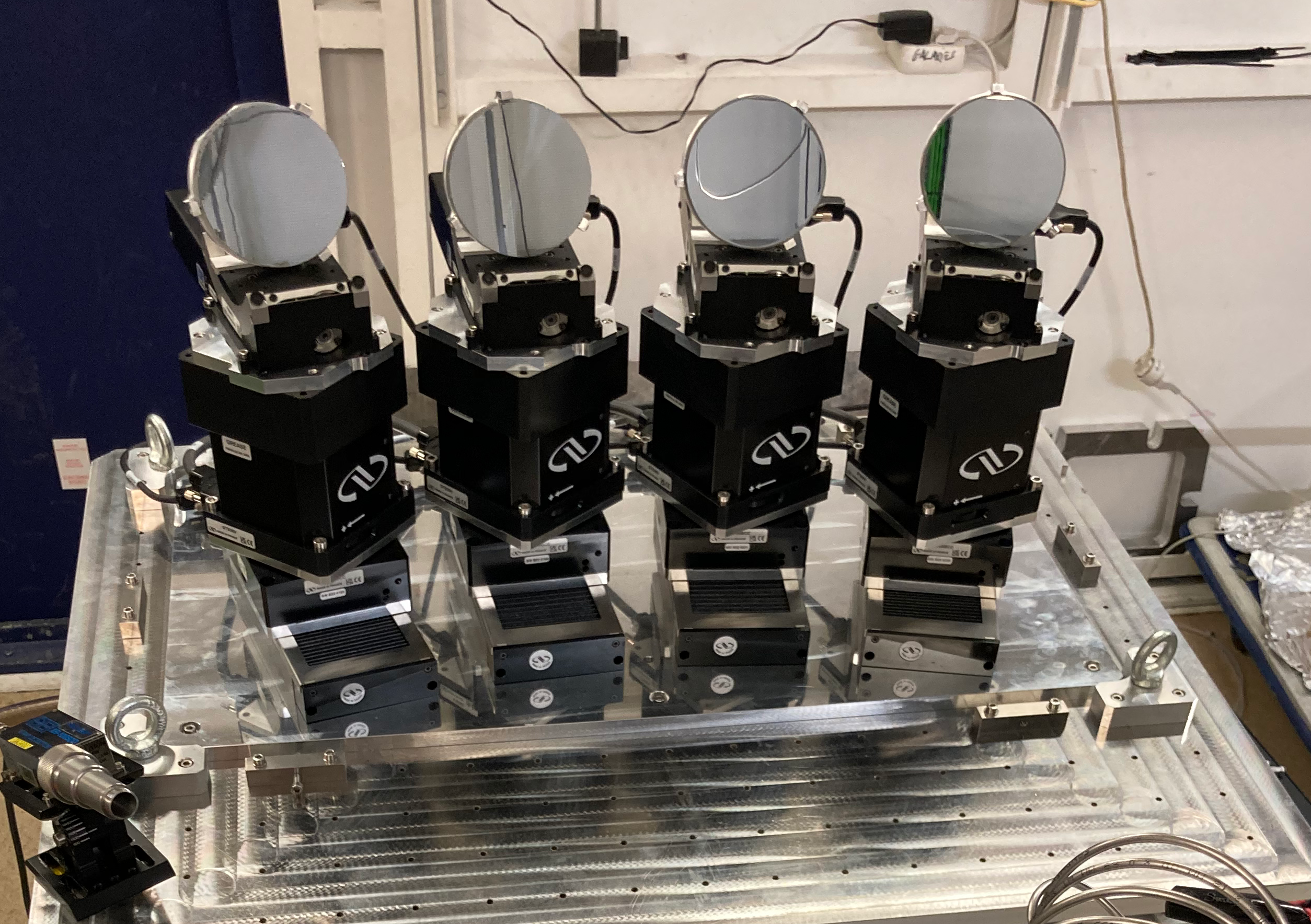
XES scanning / HERFD-XAS [MULTIXS]
4 crystals, R = 1m ou 0.5 m
Johann geometry
SDD Detector

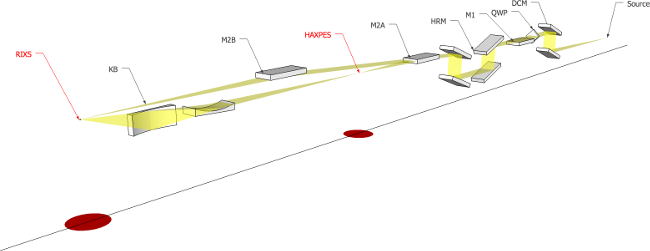
XRS [MATRIXS]
Johann geometry
Si(110), 40 analyzers, R = 1m
2D hybrid pixelated 2D detector MERLIN (© QuantumDetector)
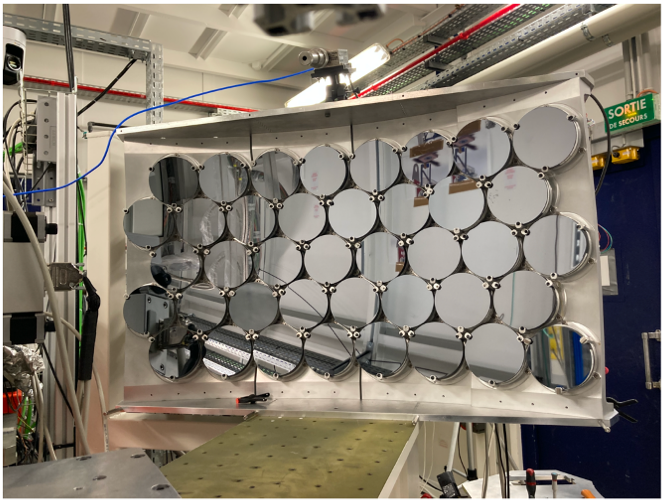
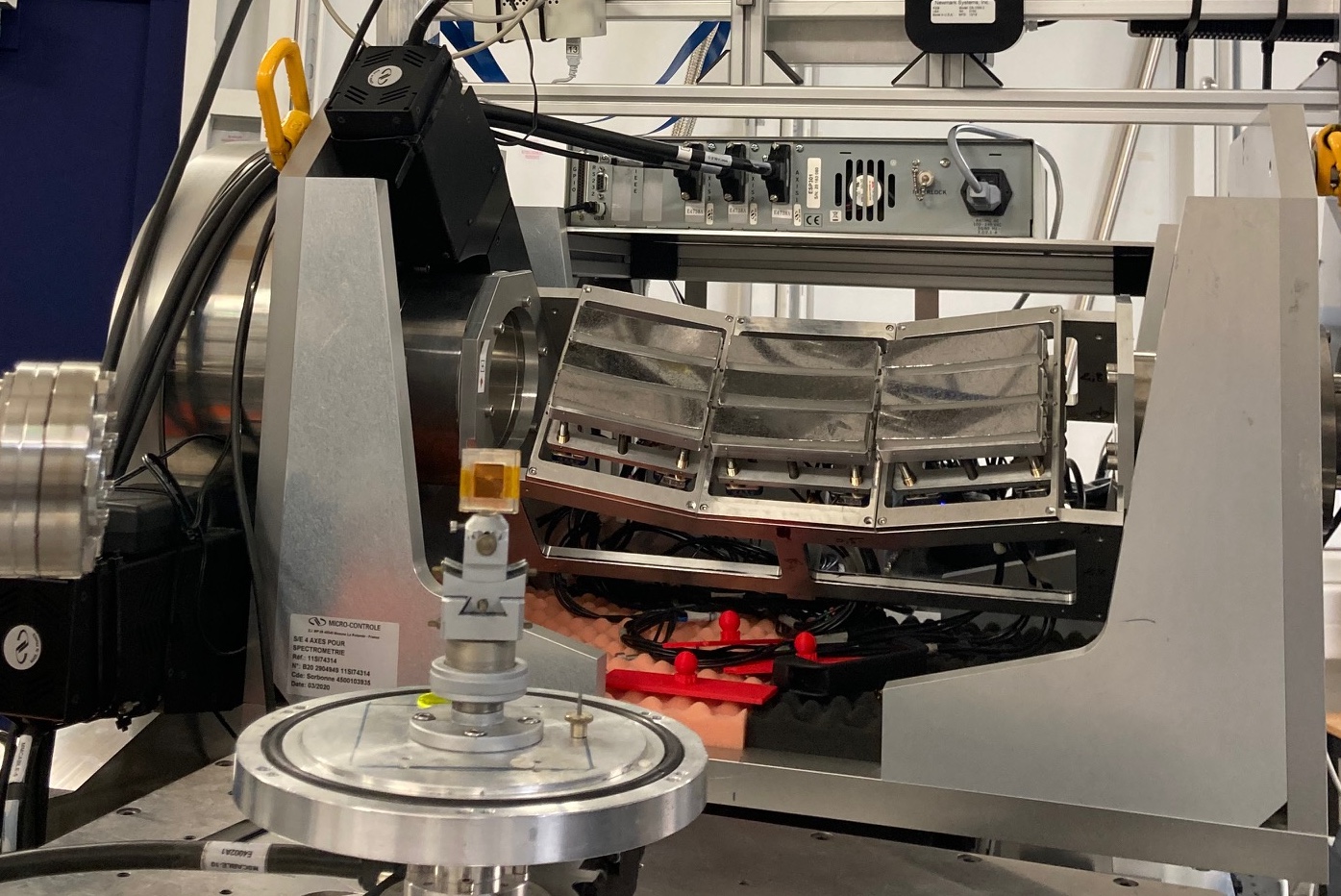
XES dispersive [VAMOXS / MOSARIX]
VAMOXS
Von Hamos dispersive geometry
8 x Si(110), 8 x Si(111), R :=0.5 m
2D hybrid pixelated 2D detector MERLIN (© QuantumDetector)
Accessible energy range : 4 - 12 keV
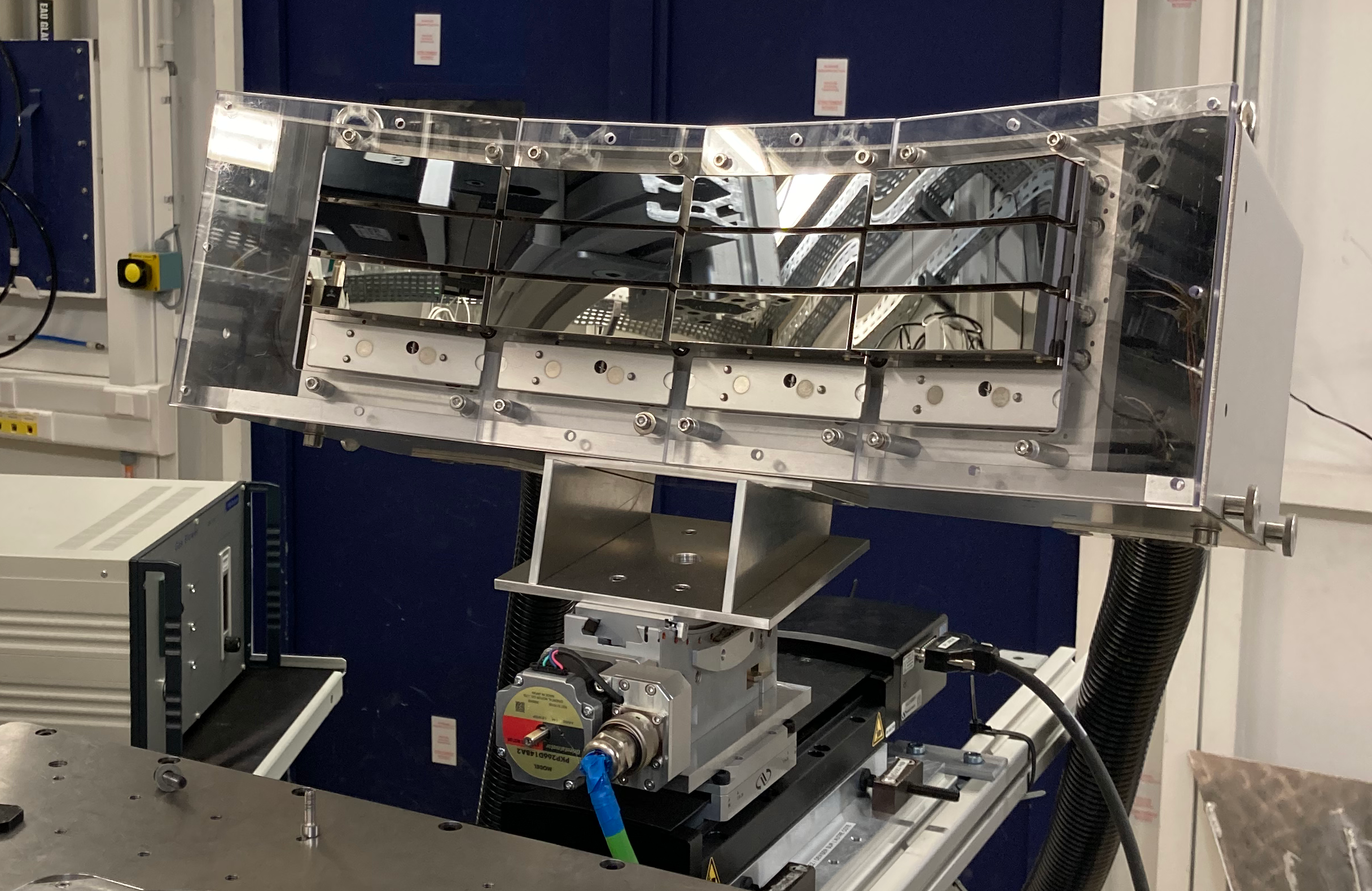

MOSARIX (Sorbonne Université)
Von Hamos dispersive geometry
2D hybrid pixelated 2D detector PILATUS 100K-M (© Dectris)
9 x HAPG graphite, R =0.5 m
Accessible energy range : 2 - 5 (12) keV

Sample Environments
- High pressure cells
- Low temperature cryostats : He flow / He closed loop / He Fast loading / He cryostat for high pressure
- High temperature
- Liquid microjet
- Liquide cell
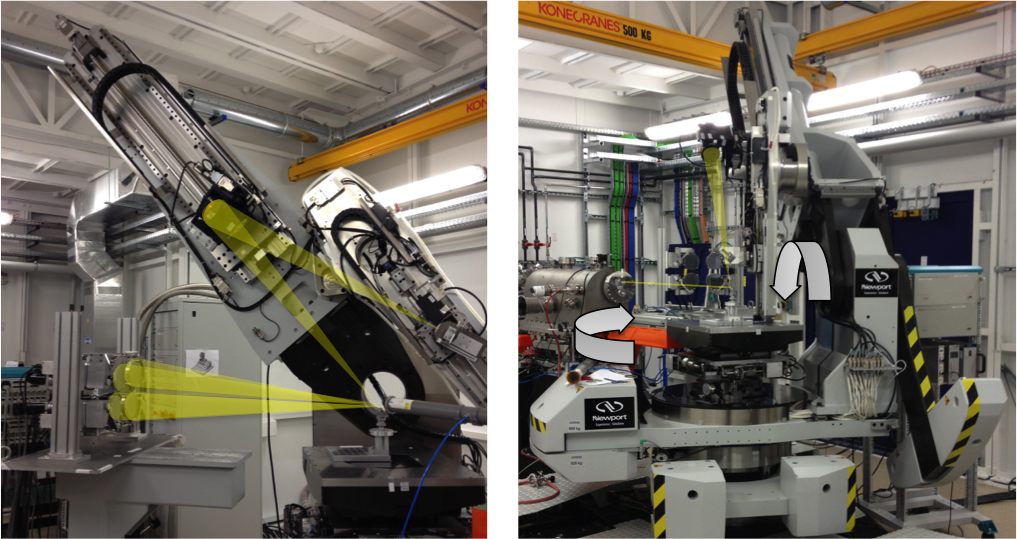
HAXPES
Instrument
Hemispherical Analyzer SCIENTA EW4000
Ec < 12 keV, resolution = 150 meV
wide acceptance angle +/- 25°
Spot size : 80 x 30 μm2 (H x V)
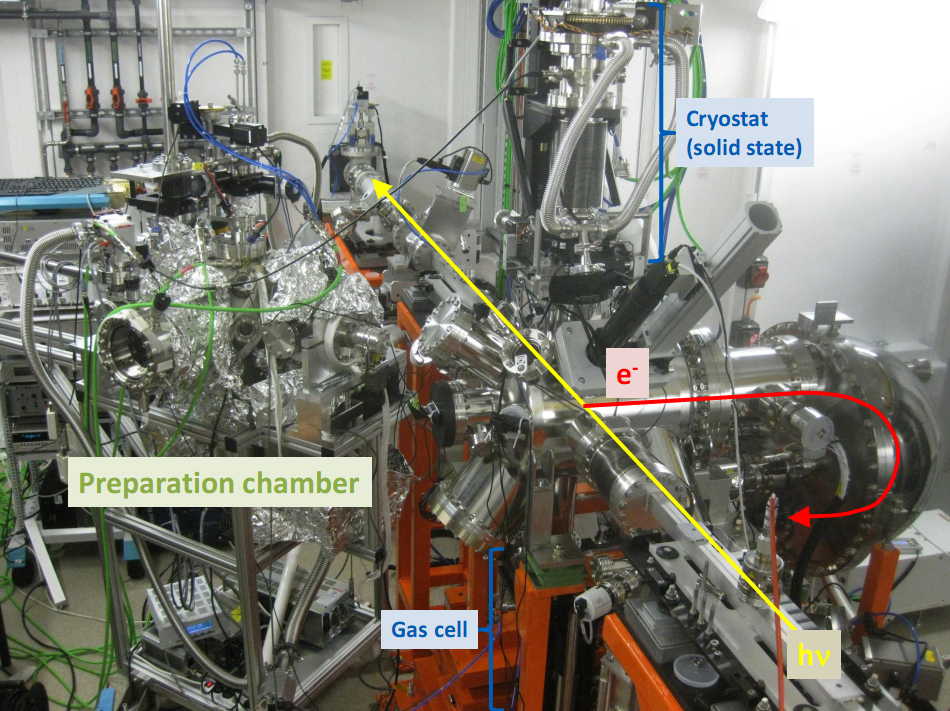
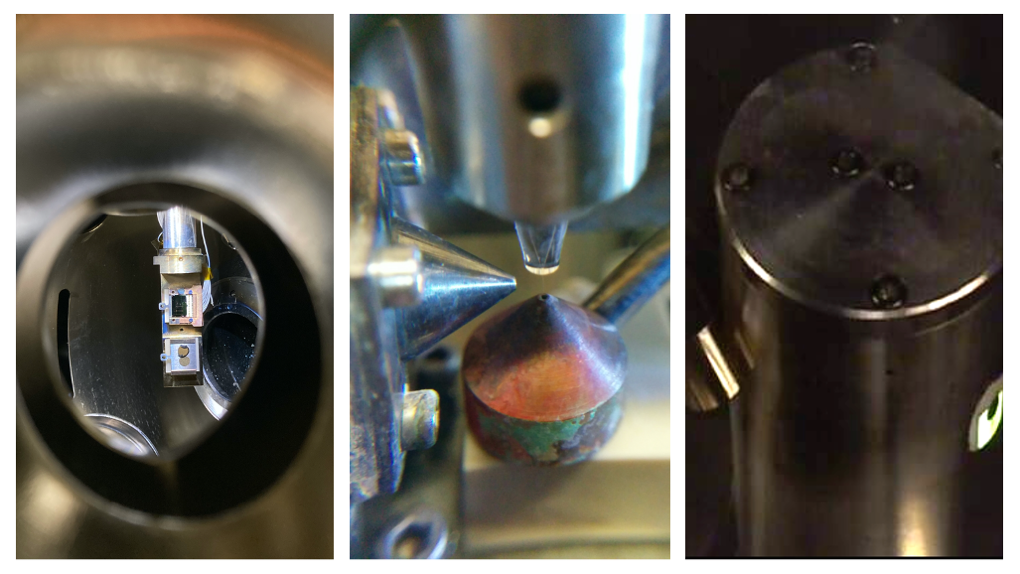
Sample preparation
- UHV cleaving
- High temperature (900 °C)
- LEED
Sample environnements UHV
- 4 axes manipulator
- Low temperature (15 K)
- High temperature (900 °C)
- In-situ bias
- Liquid microjet
- Liquid cell
- Gas cell

References
Please use the following references when using the beamline equipments
Beamline
J.-P. Rueff, J. M. Ablett, D. Céolin, D. Prieur, Th. Moreno, V. Balédent, B. Lassalle, J. E. Rault, M. Simon, and A. Shukla, The galaxies beamline at soleil synchrotron: Inelastic x-ray scattering and photoelectron spectroscopy in the hard x-ray range, J. Synchrotron Rad. 22, 175 (2015).
HAXPES
D. Céolin, J.M. Ablett, D. Prieur, T. Moreno, J.-P. Rueff, B. Pilette, T. Marchenko, L. Journel, T. Marin, R. Guillemin, and M. Simon, Hard X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy on the GALAXIES beamline at the SOLEIL synchrotron, J. Elec. Spect. Relat. Phenom. 190, 188 (2013)
RIXS
J. M. Ablett,D. Prieur, D. Céolin, B. Lassalle-Kaiser, B. Lebert, M. Sauvage, Th. Moreno, S. Bac, V. Balédent, A. Ovono, M. Morand, F. Gélebart, A. Shukla and J.-P. Rueff, 'The GALAXIES inelastic hard X-ray scattering end-station at Synchrotron SOLEIL,' J. Synchrotron Rad. 26, 2019.
MULTIXS / VAMOXS
J. M. . Ablett, A. Berlioux, D. Prieur, J. Harrison, L. Heller, S.Gliga, and J.-P. Rueff, MULTIXS: A new scanning multi-analyzer x-ray emission spectrometer at the GALAXIES beamline at synchrotron SOLEIL, Review of Scientific Instruments 96 (2025), no. 5, 053104.
J. M. Ablett, and J.-P. Rueff, High energy resolution x-ray spectroscopy for materials studies at the GALAXIES beamline, synchrotron SOLEIL: HERFD-XAS, XES, and RXES, Synchrotron Radiation News, 1–6 (2025)
MOSARIX
I. Ismail, R. Moussaoui, R. Vacheresse, T. Marchenko, O. Travnikova, R. Guillemin, A. Verma, N. Velasquez, D. Peng, H. Ringuenet, F. Penent, R. Püttner, D. Céolin, J.-P. Rueff, and M. Simon, MOSARIX: Multi-crystal spectrometer in the tender x-ray range at SOLEIL synchrotron, Review of Scientific Instruments 95 (2024), no. 5, 053103.
HRM
J.M. Ablett, J.-M. Dubuisson, T. Moreno, D. Céolin, E. Raimon, D. Prieur, D. Corruble, J. Coquet, A. Lestrade, C. Bourgoin, and J.-P. Rueff, New Design Concept for a High-Resolution In-Vacuum 4-Bounce Hard X-Ray Monochromator at the GALAXIES Beamline at the SOLEIL Synchrotron, Journal of Physics Conferences Series, 425: art.n° 052007 (2013)








